Install Postgresql
Postgresql is amongst the safest Open Source databases. Rock solid and simple to maintain - year after year. In my case it is used both as a "lookup" database (static contents) and as a "real" database (CRUD contents). The lookup database should be on localhost, but the CRUD database can be on another VPS. Note that Upcloud can connect to this "external" database by a local IP address. Every VPS on Upcloud has 2 IP-addresses. The internal IP-address can be reached only from another VPS not reachable from the outside internet.
It is not necessary to install Postgresql if you intend to only host a static web site.
1. Login to Webmin and install Postgresql
You can install Debian's "default" version of Posgresql from Un-used Modules by one click. I recommend that not use the "module configuration" as it is unpredictable.
Refresh Modules to reach the Webmin Postgresql Manager
3. Add postgres role as a sudoer
To execute sudo command the postgres must be a "sudoer"
usermod -aG sudo postgres
To check postgres it is saved as sudoer - do this command
getent group sudo
And finally update everything...
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
4. Set password for your postgres admin role
To keep Postgresql safe enough you ought to add a safe password.
Change to user postgres and psql
sudo -u postgres psql
Set password for user postgres
\password postgres
Check the new password
psql -U postgres -W
If necessary - quit
\q
5. Tell Postgresql to "listen" for outside calls
You can use Webmin > Tools > File Manager to find /etc/postgresql/13/main/postgresql.conf
Right click on the postgresql.conf and select edit. Then uncomment by erasing the "#" and enter an asterisk (star). This means that Postgresql is listening on the default port 5432 and to all incoming calls.
listen_addresses = '*'
Restart Postgresql
6. Restrict some access in pg_hba.conf
The pg_hba.conf file is used by PostgreSQL to determine which clients are allowed to connect to the server and which authentication methods should be used for each client. You can look at this file as a second firewall.
You can use Webmin > Tools > File Manager to find /etc/postgresql/13/main/pg_hba.conf
Right click on the pg_hba.conf and select edit. Replace the default settings with this suggestion (make your own settings).
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
local all postgres peer
hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
local all all peer
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5
host all all ::1/128 md5
Restart Postgresql
7. Check if port 5432 is open
Open the Terminal on your computer and check if port 5432 is open on the VPS and Postgresql is listening on this port.
nc -zv 11.111.11.111 5432
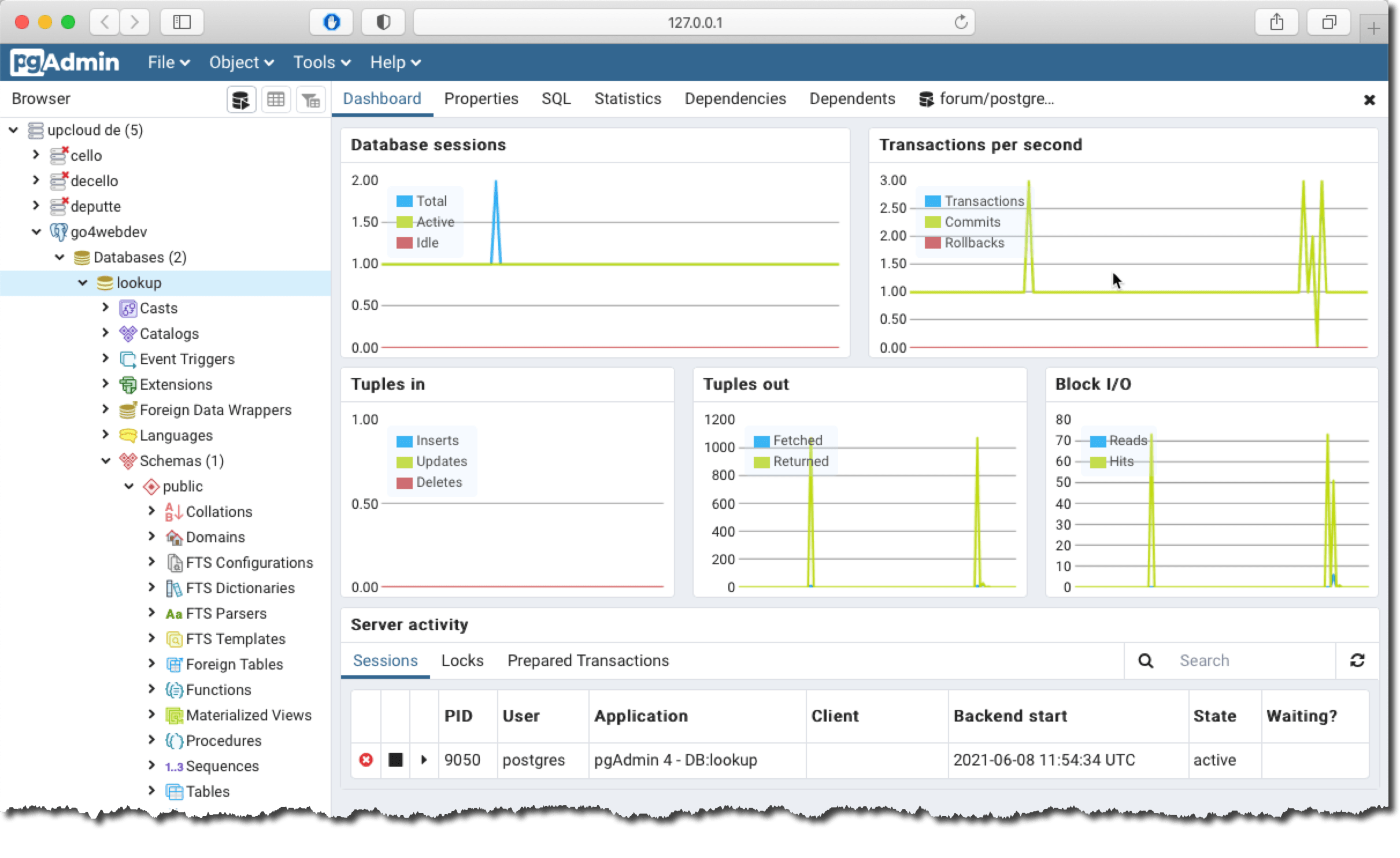
To administer Postgresql I recommend pgAdmin4 installed on your local computer. You can add Postgresql servers, monitor activities and interact with the databases.
8. Install pgAdmin4 on your computer
Here is the link to download pgAdmin: